Rabbits are more than just the cute brown bunnies you may see hopping around in your backyard. Rabbits have been kept as pets since the 19th century and are one of the most popular pets in the United States. They are a great house pet, who can become bonded to their owners like cats and dogs do. If you have an image in your mind of a white rabbit with pink eyes just sitting in a cage, that stereotype is wrong. Rabbits are intelligent pets who can quickly integrate themselves into your family. They also require more responsibility and care than other small pets like hamsters. If you’re considering adding a bunny to your family or learning about a new pet, check out our articles to learn how to care for rabbits.
Pet Rabbit Supplies and Information
You can learn more about taking care of rabbits and the supplies they need from our helpful articles.
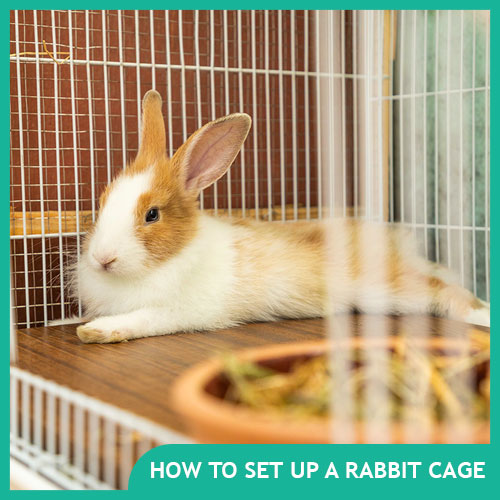
Rabbit Housing and Cages
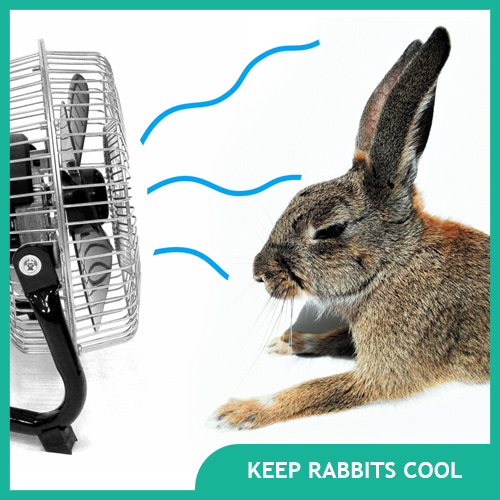
Bunny Care
Rabbit Fun and Play
Rabbit FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are rabbits good pets?
 Rabbits make great pets for people who are willing to put in the effort and investment of adding a rabbit (or a couple bunnies) to their family. While many people incorrectly assume that having a rabbit is like having a hamster or a mouse that will just sit in a cage all day, that is not true. Once a rabbit is acclimated to a family, it is more like a cat. They are litter trained and can free roam a house or any rooms that are bunny-proofed. They also require annual vet visits, which increases the cost of owning a pet rabbit.
Rabbits make great pets for people who are willing to put in the effort and investment of adding a rabbit (or a couple bunnies) to their family. While many people incorrectly assume that having a rabbit is like having a hamster or a mouse that will just sit in a cage all day, that is not true. Once a rabbit is acclimated to a family, it is more like a cat. They are litter trained and can free roam a house or any rooms that are bunny-proofed. They also require annual vet visits, which increases the cost of owning a pet rabbit.
If you think you’re interested in adding a rabbit to your family, check out our articles to get a sense of what rabbit supplies you’ll need and the special needs that a pet bunny has.
How long do rabbits live?
The lifespan for domestic rabbits is generally 8 to 12 years. Larger rabbits and purebred rabbits often have a shorter lifespan than dwarf and mixed breed rabbits. This rabbit lifespan is based on the assumption that it is an indoor house rabbit that has been spayed or neutered. An unspayed female rabbit is at a great risk of developing cancer which would be fatal. Rabbits housed outdoors also have shorter lifespans because of the increased risks and stress of living outside.
Wild rabbits have a lifespan of approximately 3 years.
The oldest rabbit on record lived to be 18 years and 10 months old (read more about Flopsy in the Guinness Book of World Records).
What do rabbits eat?
A pet rabbit’s diet consists of pellets, fresh hay, fresh vegetables, and water. Each food type is important to give your bunny a well-rounded diet that addresses all of their nutritional and health needs.
Treats are also a part of a rabbit’s diet, though they should be given sparingly. Treats can include things like fresh or dried fruit. You should generally avoid any packaged rabbit treats sold in pet stores that are high in sugars.
Read more about pet rabbit diet & nutrition.
Wild rabbits eat whatever food they have access to depending on the season. If you garden, you may notice that wild bunnies munch on your flowers, fruits, and veggies. They also eat plants like weeds and clover. During colder months, they will eat any green plants they can find as well as twigs and bark.
Should a pet rabbit be spayed or neutered?
 The answer to this questions is a big resounding YES! It’s important for your rabbit’s health and happiness to spay or neuter them once they are old enough (usually about 4-6 months old). The biggest reason to have your rabbit fixed is to prevent any unwanted baby bunnies. Rabbits are the third most euthanized pet in the United States (after cats and dogs) and breed very easily. If you plan to house male and female rabbits together or in close proximity, they must be fixed to prevent reproducing.
The answer to this questions is a big resounding YES! It’s important for your rabbit’s health and happiness to spay or neuter them once they are old enough (usually about 4-6 months old). The biggest reason to have your rabbit fixed is to prevent any unwanted baby bunnies. Rabbits are the third most euthanized pet in the United States (after cats and dogs) and breed very easily. If you plan to house male and female rabbits together or in close proximity, they must be fixed to prevent reproducing.
If you only plan on having one rabbit or only keep a same sex pair, it’s still a good idea to get your bunnies fixed. They will live longer as spaying is the only way to prevent reproductive cancer in female rabbits. It also helps extend male rabbit’s lives by eliminated sexual aggression that can lead to fights with other animals. Altered rabbits are also calmer and more loving pets. They are less liked to dig, chew, or display any other aggressive behavior. It also makes litter training a lot easier.
You can read more about spaying and neutering rabbits on the House Rabbit Society website.
Why does my rabbit chew on everything?
Rabbits, like many other small pets, are constantly chewing. This is because their teeth are always growing, so they need to chew and gnaw on hard things to wear them down and maintain a reasonable length. Rabbits cannot be trained to stop chewing since it’s a natural urge, which puts things like electrical cords, books, and floorboards at risk of chewing.
To help combat your rabbit’s chewing you should rabbit-proof any areas of your home where your bunny roams. You should also offer rabbit safe alternatives to chew. This may include cardboard boxes or toys made from rabbit safe wood. By providing safe and enticing chew options, your rabbit will be less likely to gnaw on anything you don’t want them to and will be healthier in the long run.
Learn more about how to stop rabbits from chewing.
What different names are there for rabbits?
Rabbit, bunny, and bunny rabbit are the most common names given to both wild and pet rabbits.
The scientific name is oryctolagus cuniculus.
What is a male rabbit called? A male bunny is called a “buck.”
What is a female rabbit called? A female bunny is called a “doe.”
What is a baby bunny called? Baby rabbits can be called “kits” or the simple “bunny.”
Are rabbits nocturnal?
You’ve probably seen your rabbit napping during the day and wondered why they aren’t interested in playing. Rabbits aren’t actually nocturnal. They’re actually crepuscular, meaning they’re most active around dawn and dusk–especially in the evening. This works well for most rabbit parents since they’re interested in playing in the morning and evening when many people are home from work and school. If it works with your schedule, let your rabbit sleep during the day and schedule their playtime in the evening hours.
Can I walk my pet rabbit on a leash?
While it’s super cute to see someone walking their rabbit down the street or through the park with a harness and leash, it’s actually dangerous for the rabbit! Since bunnies are prey animals they are always on guard for predators and dangerous situations. When you take a rabbit outside the home, they’re going to encounter new sights, smells, and noises. Their senses are more heightened than yours–especially their hearing. If they hear something that scares them, a rabbit’s first instinct is to run.
If a rabbit panics and tries to get away while wearing a leash, there are a number of ways they can be injured or even killed. They can choke themselves, get tangled up and break a limb or even injure their back. It’s best for rabbits to stay safe at home. If your rabbit likes to enjoy outdoor time, consider supervising them outside in an exercise pen.
I found a rabbit or a nest of baby rabbits in my backyard. Can I take care of them?
Wild rabbits are very different from their domestic cousins the house rabbits. They do not do well in a house and are hard to care for without special training and knowledge. If you find a nest of baby rabbits in your yard, leave them alone. A lot of people worry that they’ve been abandoned because they don’t see the mother nearby. The mother rabbit does this on purpose to protect her baby bunnies. She will only visit the nest when it is time to nurse them (usually twice a day at dawn and dusk). She is very clever at evading predators and will not approach the nest if you’re nearby.
To learn more about what to do about wild rabbits, the Humane Society has a very helpful article about how to handle this situation.